Cybersecurity is made up of three components: people, process, and technology. Of the three, technology is often the focus of the majority, as it is possibly the easiest element to implement. However, for a business to successfully meet its security goals, all three elements must be viewed with a systematic, flexible, and scalable approach.
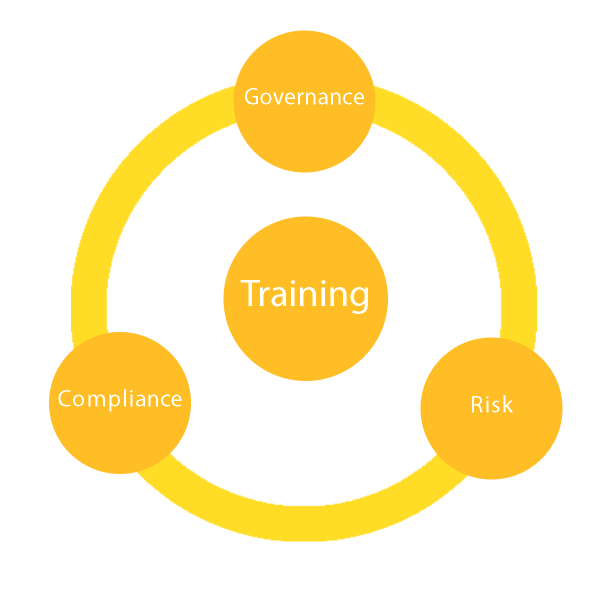
To achieve this, an effective Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) System is crucial, as it ensures that a holistic view has been taken, while tackling the daunting mission of cybersecurity. After all, automating a poorly thought-out process with state-of-the-art technology does not improve the process itself or the end results.